TFT LCD for HMI: A Comprehensive Exploration
In the rapidly evolving landscape of technology, the importance of user interfaces cannot be overstated. At the heart of many modern Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs) lies the Thin-Film Transistor Liquid Crystal Display (TFT LCD). This technology has revolutionized the way users interact with machines, making interfaces more intuitive, responsive, and visually appealing. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of TFT LCDs, exploring their features, advantages, applications, and future trends.
Understanding TFT LCD Technology
TFT LCDs are a specific type of liquid crystal display that utilizes thin-film transistor technology to enhance image quality and responsiveness. Unlike traditional LCDs that rely on a passive matrix for controlling pixels, TFT LCDs employ an active matrix, where each pixel is controlled by a thin film transistor. This arrangement allows for faster refresh rates and improved contrast, making it ideal for dynamic content often found in HMI applications.
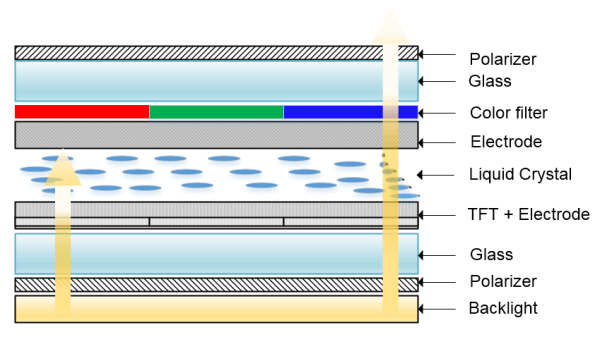
The construction of a TFT LCD involves several layers, including a backlight, liquid crystal layer, and the TFT array. The backlight provides illumination, while the liquid crystal layer modulates the light to create images. The TFT array, placed behind the liquid crystal layer, enables precise control over each pixel, resulting in sharp and vibrant visuals. This combination of layers not only enhances the display quality but also ensures that the interface remains legible in various lighting conditions.
Advantages of TFT LCDs in HMI Applications
One of the most significant advantages of TFT LCDs is their ability to produce high-resolution images with excellent color reproduction. This capability is crucial for HMIs, where clarity and detail can significantly impact user experience. Whether in industrial settings, medical devices, or consumer electronics, the vibrant colors and sharp images produced by TFT LCDs ensure that users can easily read and interpret information.
Moreover, TFT LCDs offer a wide viewing angle, which is essential for HMIs that may be viewed from different positions. Users are often required to interact with these interfaces at various angles, and the ability of TFT displays to maintain consistent color and brightness across a wide viewing angle enhances usability. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in collaborative environments where multiple users might engage with the same interface.
Another notable advantage is the responsiveness of TFT LCDs. The technology allows for quick refresh rates, meaning that changes in the interface can be displayed almost instantaneously. This responsiveness is critical in applications where real-time feedback is necessary, such as in automotive displays or interactive kiosks. Users can navigate menus and access information without noticeable delays, contributing to a more seamless interaction.
Applications of TFT LCDs in HMIs
The versatility of TFT LCDs makes them suitable for a wide range of applications in HMIs. In industrial automation, for instance, TFT displays are used in control panels and monitoring systems. Operators can visualize data in real-time, making it easier to monitor processes and make informed decisions quickly. The ability to customize the interface further allows industries to tailor the HMI to specific operational needs.
In the automotive sector, TFT LCDs have become increasingly prevalent in dashboards and infotainment systems. Drivers benefit from high-resolution displays that provide critical information such as speed, navigation, and multimedia controls. The integration of touch capabilities in TFT displays enhances the interactive experience, allowing drivers to access features with simple gestures, thereby improving safety and usability.
Medical devices also leverage TFT LCD technology to deliver essential information to healthcare professionals. Whether displayed on patient monitors or diagnostic equipment, the clarity and responsiveness of TFT LCDs ensure that critical data is presented accurately and promptly. This capability is vital in medical settings, where timely information can significantly impact patient care and outcomes.
Future Trends in TFT LCD Technology for HMI
As technology continues to advance, the future of TFT LCDs in HMI applications looks promising. One emerging trend is the integration of advanced touch technologies. Capacitive touchscreens, for instance, are becoming increasingly common, allowing for more intuitive user interactions. The combination of TFT displays with touch capabilities enables a more dynamic and engaging user experience, paving the way for innovative applications.
Another trend is the development of flexible TFT LCDs. These displays can be bent or shaped to fit unique form factors, expanding the possibilities for HMI design. In industries such as consumer electronics, where aesthetics play a crucial role, flexible displays could lead to more creative and visually appealing product designs.
Additionally, advancements in energy efficiency are becoming a focal point in the development of TFT LCDs. With the growing emphasis on sustainability, manufacturers are exploring ways to reduce power consumption without compromising performance. This shift is particularly relevant in portable devices where battery life is a critical consideration. Also, most HMI devices are fanless, low power consumption and less heat release are important.
Conclusion
In summary, TFT LCD technology has become a cornerstone of modern Human-Machine Interfaces, offering a blend of high-quality visuals, responsiveness, and versatility. As industries continue to evolve, the demand for intuitive and engaging user interfaces will only increase, positioning TFT LCDs as a vital component in the future of HMI design. By understanding the intricacies of this technology and its applications, businesses can harness its potential to enhance user experiences and drive innovation in their respective fields. Through continuous advancements, TFT LCDs are set to remain at the forefront of HMI technology, leaving behind traditional interfaces and paving the way for a more interactive and visually engaging future.
